Effective media planning is essential for maximizing your brand’s reach, engagement, and return on investment in the ever-evolving advertising landscape. At The Media Ant, we understand that the right media strategy can be the difference between a successful campaign and a missed opportunity. Media planning plays a pivotal role in the success of any marketing campaign by serving as the strategic blueprint for how advertisers effectively reach their target audience. Understanding media planning is crucial for businesses looking to cut through the noise and build meaningful connections with customers. This article will cover the definition of media planning, explore its various types, and emphasize its importance in modern marketing.
What is Media Planning?
Media planning is the strategic process of determining how and where to allocate advertising resources to effectively reach a target audience. It involves analyzing consumer demographics, market trends, and media consumption habits to select the most suitable channels for delivering brand messages. By identifying optimal platforms, such as television, radio, print, digital, or social media, media planners aim to maximize the impact of advertising campaigns within allocated budgets. This meticulous approach ensures that marketing efforts resonate with the right audience, driving desired outcomes and maximizing ROI.

Key Elements of Media Planning
- Audience Analysis: Understand who your audience is—their demographics, behaviors, and media habits. This insight helps identify where and how to reach them effectively.
- Media Selection: Choose the best mix of media channels, such as TV, radio, digital, print, and outdoor ads, to maximize impact. Each type of media serves different campaign goals.
- Budget Allocation: Decide how to allocate your advertising budget across these channels, balancing cost with potential reach and effectiveness.
- Timing and Scheduling: Plan when and how often your ads should run, factoring in seasonal trends and the ideal duration and frequency for maximum effectiveness.
- Creative Consideration: Ensure your ad content resonates with your audience and fits well within the selected platforms. Engaging, relevant content is key to capturing attention.
- Performance Measurement: Track the performance of your media campaigns using metrics like reach, impressions, click-through rates, and conversions to assess success and make adjustments.
At The Media Ant, we simplify and optimize the media planning process for businesses. Our platform offers a variety of media options and expert insights to help you make smart decisions and run successful campaigns.
By understanding and applying these principles of media planning, you can make sure your marketing efforts are well-targeted, cost-effective, and successful.


Source: MyHoardings
Why Do You Need a Media Plan?
A media plan is crucial for getting the most out of your advertising efforts. Here’s why it’s so important:
1. Reach the Right People
A good media plan helps you target your audience effectively, ensuring your ads are seen by the right people on the right platforms.
2. Optimized Budget Allocation
By analyzing audience demographics, media consumption habits, and market trends, media planning allows advertisers to allocate resources efficiently, minimizing waste and maximizing ROI.
3. Perfect Timing
Knowing when to run your ads is key. A media plan helps you schedule your ads to reach your audience at the most effective times.
4. Consistent Branding
A media plan ensures your advertising is consistent across all platforms. This helps build a strong, unified brand identity.
5. Track and Improve
With a media plan, you can measure how well your ads are doing. This allows you to see what’s working and make adjustments to improve your results.
6. Make Smart Decisions
A media plan provides a clear strategy for your advertising. It helps you decide which channels to use, what kind of content to create, and how to target your audience effectively.
7. Stay Focused
Having a media plan keeps your advertising efforts organized and efficient. It helps you focus on the most impactful strategies, saving time and money.
8. Campaign Effectiveness
Media planning lays the groundwork for successful advertising campaigns by defining clear objectives, identifying key performance indicators (KPIs), and developing tailored strategies to achieve desired outcomes.
At The Media Ant, a solid media plan is key to successful marketing. Our platform gives you the tools and insights to create and execute a media plan that delivers real results.
Media Planning Process
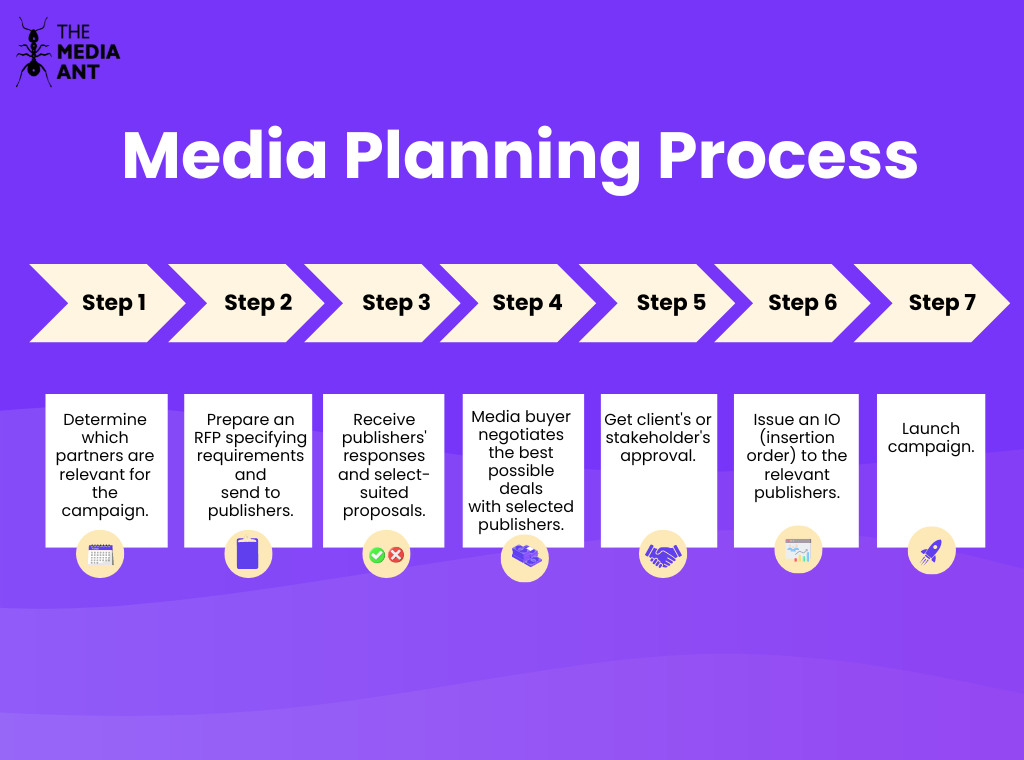
The Media Planning Process involves a series of steps to ensure that advertising campaigns are effective and reach the intended audience. Here’s an explanation of each step:
Step 1: Determine Which Partners Are Relevant for the Campaign
The first step in the media planning process is to identify potential media partners who can help achieve the campaign’s objectives. This involves researching various publishers, platforms, and channels to determine which ones align with the target audience, campaign goals, and budget.
Step 2: Prepare an RFP Specifying Requirements and Send it to the Publishers
Once potential partners are identified, a Request for Proposal (RFP) is prepared. The RFP outlines the campaign’s requirements, including target audience, objectives, budget, timeline, and any specific creative or technical specifications. The RFP is then sent to the selected publishers or media outlets.
Step 3: Receive Publishers’ Responses and Select Suited Proposals
After sending out the RFP, responses from publishers are reviewed. These responses typically include detailed proposals that explain how the publishers plan to meet the campaign’s requirements. The media planner evaluates these proposals based on factors such as audience reach, cost, and alignment with campaign goals, and selects the most suitable ones.
Step 4: Media Buyer Negotiates Best Possible Deals with Selected Publishers
Once suitable proposals are selected, the media buyer negotiates with the chosen publishers to secure the best possible deals. This negotiation process involves discussing pricing, ad placements, added value opportunities, and objectives, including their pricing, audience reach, ad formats, and any added value they can provide. The media planner evaluates these proposals to select the ones that best match the campaign’s goals and budget.
Step 5: Get the Client’s or Stakeholder’s Approval
After negotiations, the proposed media plan and deals are presented to the client or stakeholders for approval. This step ensures that all parties are aligned on the strategy, budget, and expected outcomes before moving forward.
Step 6: Issue an IO (Insertion Order) to the Relevant Publishers
With the client’s or stakeholder’s approval, an Insertion Order (IO) is issued to the selected publishers. The IO is a formal agreement that outlines the specifics of the ad placements, including the agreed-upon terms, schedule, and payment details.
Step 7: Launch Campaign
The final step is to launch the campaign according to the plan. This involves coordinating with the publishers to ensure that ads are placed correctly and on time. During the campaign, performance is monitored to ensure that it meets the set objectives, and adjustments may be made as necessary based on real-time data and feedback.
This structured approach helps ensure that media campaigns are well-planned, cost-effective, and capable of achieving the desired reach and impact.
Factors Influencing Media Planning
Media planning is a multifaceted process influenced by various factors that shape the strategic decisions of advertisers. Three key factors that significantly impact media planning are audience analysis, budget considerations, and market research and trends.
1. Audience Analysis
Understanding the target audience is paramount in media planning. Factors such as demographics, psychographics, behaviors, and media consumption habits play a crucial role in determining which media channels are most effective for reaching and engaging with the desired audience. By conducting thorough audience analysis, media planners can tailor their strategies to align with the preferences and characteristics of their target demographic, ensuring that advertising efforts resonate and drive meaningful interactions.
2. Budget Considerations
Budget considerations are central to media planning, as they dictate the scope and scale of advertising campaigns. Media planners must carefully allocate resources across various media channels to maximize reach and impact while staying within budget constraints. Factors such as advertising costs, media rates, and potential return on investment (ROI) are taken into account when determining budget allocations. Effective budget management ensures that resources are optimally utilized to achieve campaign objectives and deliver a strong ROI.
3. Market Research and Trends
Market research and trends provide invaluable insights into the evolving landscape of consumer behavior, industry dynamics, and emerging media platforms. Media planners continuously monitor market trends, competitor strategies, and technological advancements to stay ahead of the curve and adapt their approaches accordingly. By staying abreast of shifts in consumer preferences and media consumption patterns, media planners can identify new opportunities, anticipate challenges, and optimize their strategies to capitalize on emerging trends effectively.
Media Planning vs. Media Buying: What’s the Difference?
People often mix up media planning and media buying, thinking they’re the same thing. While they’re closely related, they play different roles in creating a successful advertising campaign. Let’s break down what each one does and how they work together.
What is Media Planning?
Media planning is like the roadmap for your advertising campaign. It’s where you figure out:
- Who You’re Targeting: You need to know your audience—who they are, what they like, and where they spend their time.
- Where to Advertise: Based on your audience, you choose the best platforms, like TV, radio, social media, or websites, to reach them.
- What You Want to Achieve: Whether it’s boosting brand awareness or driving sales, you set clear goals for your campaign.
- How to Spend Your Budget: You decide how much money to allocate to each platform to get the best results.
- When to Run Your Ads: Timing is key, so you plan when your ads will be most effective to reach your audience.
In short, media planning is all about strategizing. It’s the big-picture thinking that lays out the best way to connect with your audience and achieve your goals.
What is Media Buying?
Once the plan is set, media buying is where the action happens. It involves:
- Negotiating Deals: You work with media outlets to get the best prices and prime ad placements, whether it’s a TV spot, a social media ad, or a banner on a website.
- Placing the Ads: This is when you purchase the ad space or time slots and make sure your ads are shown to your target audience.
- Tracking and Tweaking: After the ads are live, you monitor how they’re performing and make any necessary adjustments to improve results, like shifting budgets or changing placements.
Media buying is all about execution. It’s the hands-on work that ensures your ads reach the right people at the right time and for the right price.
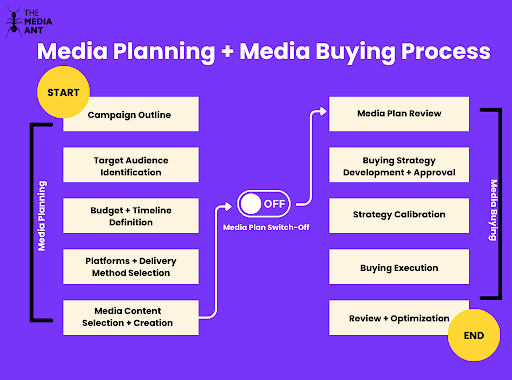
How They Work Together
Media planning and media buying are like two sides of the same coin. Media planning sets the strategy, and media buying brings that strategy to life. Without a good media plan, your ad spend can go to waste. And even with a great plan, if the buying isn’t done right, your ads might not reach their full potential.
At The Media Ant, we make sure both media planning and media buying work hand in hand to create campaigns that hit the mark. We help you design a solid strategy and then execute it efficiently to get the best possible results.
Types of Media
When it comes to advertising, understanding the different types of media is key to reaching your audience effectively. Each type offers unique benefits, and knowing how to use them can make a big difference in your campaign’s success. Here’s a look at the main types of media:
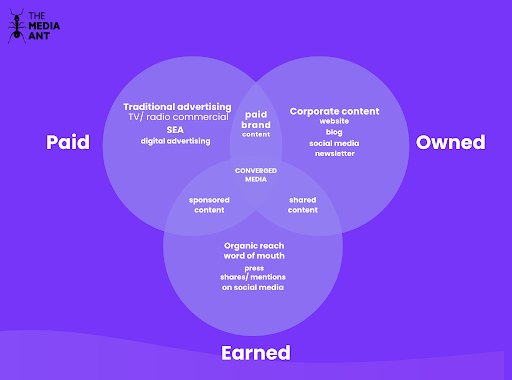
1. Paid Media
Paid media refers to any form of advertising that you pay for. It’s a quick way to get your message in front of a large audience. Examples include:
- Search Ads: Ads that appear at the top of search engine results.
- Social Media Ads**: Paid posts or sponsored content on platforms like Facebook, Instagram, LinkedIn, and Twitter.
- Display Ads**: Banners or videos on websites that target specific audiences.
- Influencer Marketing**: Paying influencers to promote your brand to their followers.
Why Use Paid Media?
It allows you to quickly reach a large, targeted audience, driving traffic, leads, or sales.
2. Owned Media
Owned media includes all the channels you control. These are platforms where you can create and distribute your content directly. Examples include:
- Your Website**: The central hub of your online presence.
- Blogs: A way to share valuable content, improve SEO, and engage your audience.
- Email Newsletters: Direct communication with your subscribers, perfect for promotions and updates.
- Social Media Profiles: Your brand’s official pages on platforms like Facebook, LinkedIn, and Instagram.
Why Use Owned Media?
It’s cost-effective and gives you full control over your brand’s message and how it’s presented.
3. Earned Media
Earned media is the exposure you gain through word-of-mouth. It’s any publicity that you haven’t paid for, often generated by happy customers, industry influencers, or media coverage. Examples include:
- Press Coverage: Articles, news stories, or features about your brand in media outlets.
- Social Media Mentions: Organic mentions, shares, and comments on social platforms.
- Online Reviews: Customer reviews and ratings on sites like Google, Yelp, or industry-specific platforms.
- Word-of-Mouth: Recommendations and referrals from satisfied customers.
Why Use Earned Media?
It’s seen as more credible and trustworthy by consumers, as it’s driven by others’ positive experiences with your brand.
4. Shared Media
Shared media is a bit of a blend between owned and earned media. It’s content that’s created by your brand but is shared or co-created with others, particularly on social platforms. Examples include:
- Social Media Engagement: Content that your audience shares or engages with on social platforms.
- User-Generated Content: Content created by your customers or followers, like photos, videos, or reviews that they share on their own profiles.
Why Use Shared Media?
It amplifies your reach and creates a community around your brand, fostering deeper connections with your audience.
5. Traditional Media
Traditional media includes the more classic forms of advertising, which are still powerful in reaching specific audiences. Examples include:
- Television: Broad reach and high impact, especially for brand building.
- Radio: Great for local targeting and reaching people on the go.
- Print Media: Newspapers, magazines, and brochures, ideal for detailed content and niche audiences.
- Out-of-Home (OOH) Media: Billboards, transit ads, and posters, effective for reaching a large number of people in high-traffic areas.
Why Use Traditional Media?
It’s highly effective for mass awareness and can complement digital efforts by reinforcing your brand’s presence.
Each type of media plays a unique role in your overall media strategy. By understanding how to use them effectively, you can create a well-rounded campaign that maximizes your reach and impact. At The Media Ant, we help you navigate these options to build a strategy that delivers real results.
Different Types of Media Channels
In advertising, media channels are the platforms you use to get your message to your audience. Each channel has its own strengths, and understanding how to use them effectively can help you achieve your marketing goals. Here’s an overview of the different types of media channels:
1. Television
Television remains one of the most powerful media channels for reaching a broad audience. It’s effective because:
- Mass Reach: Television can reach millions of people at once, making it ideal for brand awareness.
- Visual Impact: The combination of visuals, sound, and motion makes TV ads memorable and engaging.
Use TV for: High-impact campaigns, product launches, and brand building.
2. Radio
Radio is a classic medium, especially useful for local advertising. It’s effective because:
- Local Targeting: You can reach specific regions or communities.
- Mobility: People listen to the radio while driving, working out, or on the go.
Use Radio for: Local promotions, event advertising, and reaching people during their daily commutes.
3. Print Media
Print media includes newspapers, magazines, brochures, and flyers. While digital media has grown, print still holds value:
- Detailed Content: Perfect for in-depth articles, educational content, and detailed advertisements.
- Niche Audiences: Specialty magazines and local newspapers cater to specific interests and demographics.
Use Print Media for: Targeting niche markets, providing detailed information, and enhancing credibility.
4. Digital Media
Digital media covers anything online, offering a broad and versatile range of options. This includes:
- Social Media: Platforms like Facebook, Instagram, Twitter, and LinkedIn, where you can directly engage with your audience.
- Search Engines: Google, Bing, and others, where ads appear in search results.
- Websites and Blogs: Your own site or others where you can place ads or share content.
Use Digital Media for: Highly targeted campaigns, interactive content, and real-time performance tracking.
5. Out-of-Home (OOH) Media
Out-of-home media refers to advertising that reaches people when they are outside their homes. This includes:
- Billboards: Large, eye-catching ads placed in high-traffic areas.
- Transit Ads: Ads on buses, trains, subways, and in stations.
- Street Furniture: Ads on benches, bus shelters, and other public spaces.
- Airport Advertising: Ads displayed in airports, reaching a diverse and often affluent audience during travel.
Use OOH Media for Broad reach in urban areas, brand visibility, driving local foot traffic, and targeting travelers in airports.
6. Cinema
Cinema advertising targets audiences in movie theaters. It’s a unique channel because:
- Captive Audience: People are focused and less likely to skip ads.
- High Engagement: The large screen and immersive experience make ads more impactful.
Use Cinema to: target specific demographics, especially in urban areas, and create visually powerful campaigns.
7. Influencer Marketing
Influencer marketing uses individuals with large followings on social media to promote your brand:
- Trusted Voices: Influencers are seen as relatable and credible by their followers.
- Targeted Reach: You can select influencers who appeal to specific niches.
Use Influencer Marketing to: build credibility, reach niche markets, and create authentic content.
8. Sports Marketing
Sports marketing leverages the popularity of sports events, teams, and athletes to promote brands. It’s highly effective because:
- Passionate Audiences: Sports fans are highly engaged and loyal to their teams.
- Wide Reach: Sporting events often have large, diverse audiences both in person and via broadcasts.
- Association with Success: Aligning with successful teams or athletes can boost your brand’s image.
Use Sports Marketing for Brand visibility during major sporting events, sponsorships, and connecting with passionate fan bases.
Each media channel brings something unique to the table. By understanding how to use them effectively, you can create a balanced media strategy that connects with your audience in multiple ways. At The Media Ant, we guide you in choosing the right channels to achieve your advertising goals.
Conclusion
In conclusion, media planning stands as a cornerstone of effective marketing strategies in the contemporary digital age. By meticulously analyzing target demographics, selecting appropriate media channels, and optimizing budget allocations, businesses can enhance their visibility, amplify brand messaging, and ultimately drive desired consumer actions. As technology continues to reshape the media landscape, the role of media planning will only become more complex and crucial. Therefore, embracing its principles and leveraging its methodologies will be imperative for organizations striving to thrive in an increasingly competitive marketplace.

FAQs on Media Planning
1. What are the five steps in the media planning process?
The five steps in the media planning process are:
– Set objectives and goals.
– Conduct research and gather data.
– Define the target audience.
– Develop a media plan.
– Implement and evaluate the plan’s effectiveness.
2. Is media planning a skill?
Yes, media planning is a skill that involves analyzing data, understanding target audiences, selecting appropriate media channels, and developing strategies to effectively communicate messages. It requires a combination of creativity, analytical thinking, and strategic decision-making.
3. What are the elements of media planning?
The elements of media planning include setting objectives, conducting market research, defining target audiences, selecting appropriate media channels, determining budget allocation, scheduling ad placements, creating the media plan, implementing it, and evaluating its effectiveness through metrics and analytics.
4. What are media objectives?
Media objectives are specific goals set by advertisers to achieve through their media campaigns. These objectives outline what the advertising aims to accomplish, such as increasing brand awareness, driving sales, reaching a target audience, or generating leads, within a defined timeframe.
5. What is a flowchart in media planning?
In media planning, a flowchart visually represents the sequence of steps involved in the planning and execution of advertising campaigns. It outlines the process from setting objectives to selecting media channels, scheduling ad placements, and evaluating campaign effectiveness.





